

You can do this through creating personalized meal plans, suggesting different exercises, or monitoring water intake, but if you don’t know their specific energy needs, you won’t be able to give precise nutritional guidance. For instance, an athlete will have different energy needs than a sedentary adult, so you need to evaluate each client to create a plan that works for them. What works for one person may not work for someone else, so you have to work with each client individually to assess their needs and goals. Since everyone is unique and has different nutritional needs and health goals, you can’t just create a blanket recommendation and expect it to work for all of your clients. Why should you use the Harris-Benedict equation calculator?Īs a dietitian, it’s your responsibility to make sure that each client’s nutritional needs are met.
You should work with each client to make sure their nutritional needs and health goals are being met, but you may need to increase or decrease this number depending on how they feel.

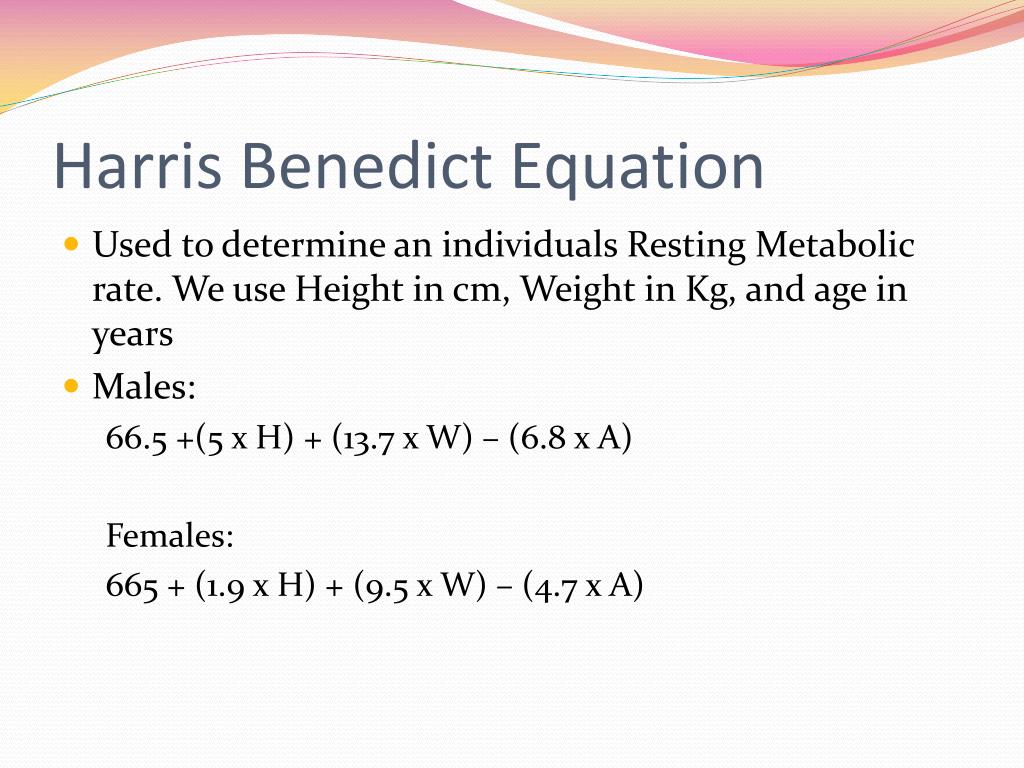
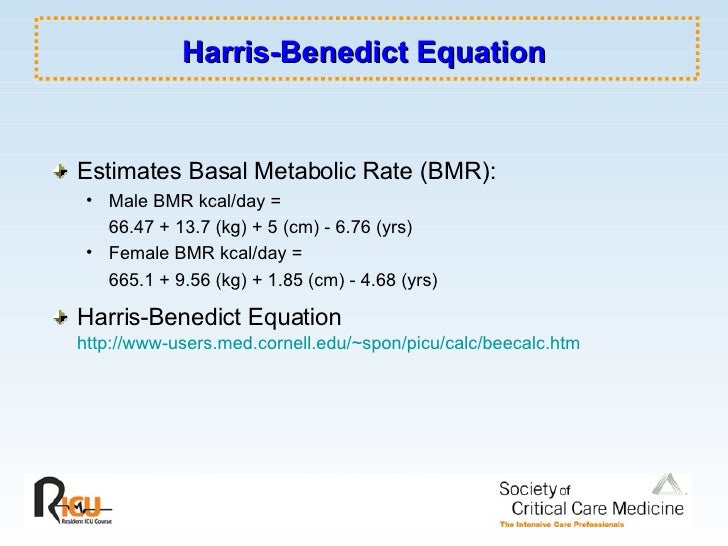
However, keep in mind that this number is just an estimate and should be used as a guideline, not a rule. This will leave you with an estimated number for your client’s daily caloric needs. Extra active–very hard daily exercise/sports & physical job or 2X day training (BMR x 1.9).Very active–hard exercise/sports 6-7 days/week (BMR x 1.725).Moderately active–moderate exercise/sports 3-5 days/week (BMR x 1.55).Light activity–light exercise/sports 1-3 days/week (BMR x 1.375).Sedentary–little or no exercise (BMR x 1.2).Step 2: Take the BMR number and multiply it by the appropriate activity factor. Women: BMR = 655 + (9.6 X weight in kilos) + (1.8 X height in cm) – (4.7 x age in years).Men: BMR = 66 + (13.7 x weight in kilos) + (5 x height in cm) – (6.8 x age in years).To use the Harris Benedict equation, you have to determine your client’s BMR and then apply an activity factor to get an estimated number for their daily caloric needs. However, this may not be fully accurate for certain people, as this equation doesn’t take into consideration lean body mass and the ratio of muscle-to-fat. The Harris-Benedict equation is a formula that uses a person’s height, weight, age, and gender to calculate their basal metabolic rate (BMR). What is the Harris-Benedict equation calculator? But what is it, why is it important, and how can you use it in your nutrition practice? Here’s what you need to know. You can do this by using the Harris-Benedict equation calculator, which uses your client’s BMR to determine caloric requirements. Here’s what you need to know about BMR, and how you should use the Harris-Benedict equation calculator.Īs a nutrition professional, it’s important to accurately assess your client’s calorie and nutrient requirements to ensure that you provide the best nutritional care possible. The Harris-Benedict equation calculator is a helpful tool that can help you create personalized meal plans to fit each client's nutritional needs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
